You may already know about climate change, sustainable energy, and sustainable development goals (SDGs). However, as we transition to sustainable energy, It is worth delving deeper into what it truly means and how it influences our environment and communities.
Understand Sustainable Energy and Renewable Energy in Seconds
In a nutshell, sustainable energy refers to all kinds of environment-friendly energy. Unlike fossils such as oil, coal, natural gas, etc., that may run out in the future, they least pollute and can not be depleted forever. It is very similar to renewable energy, however, renewable energy uses naturally replenishing resources from the earth, such as Biomass from plants.
Examples of popular sustainable energy sources include:

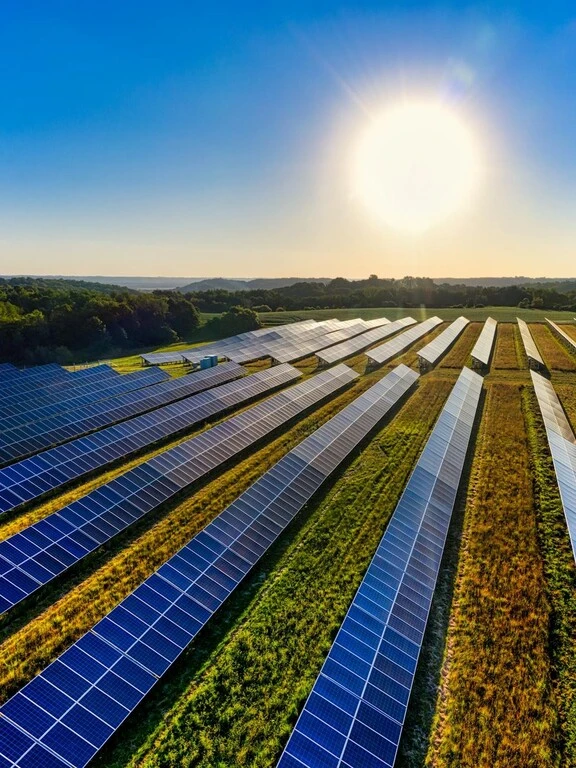
- Solar Energy
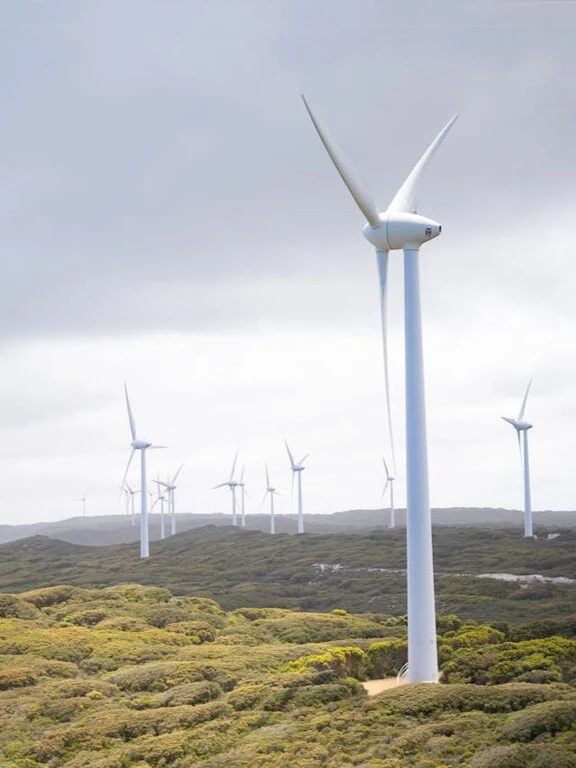
This source is radiation from the sun that can be converted into electricity using solar panels. It is widely adopted by individuals around the world. - Wind Energy
Wind power is generated by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical power - Hydropower
This energy is derived from flowing water, such as that from a reservoir or river, and is converted into electricity using spinning turbines and generators.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)
In 2015, the United Nations (UN) established the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to unite nearly 200 countries in achieving 17 goals by 2030 for a better and more sustainable future.
These goals address various aspects, including poverty, food, natural resources, health, education, gender equality, energy, and the economy, with sustainability being one of the most crucial goals.
According to the UNDP, there are five key targets in SDG No. 7:
- By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services.
- By 2030, substantially increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, promoting investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
- By 2030, expand infrastructure and upgrade technology for modern and sustainable energy services, especially in developing countries, least developed countries, small island developing states, and landlocked developing countries.

By 2030, we can expect the following:
- A significant increase in the global proportion of renewable energy compared to fossil fuels, with costs becoming lower than fossil energy.
- Enhanced cooperation among organizations and communities in producing and efficiently consuming renewable energy, leading to new clean energy businesses.
- New guidelines and regulations supporting clean energy initiatives.
- Advancements in technology and AI for sustainable energy services in isolated and developing areas.
ESG
We previously discussed the global goals. Now, the question is how to determine whether we are achieving these goals. This is where ESG comes into play.
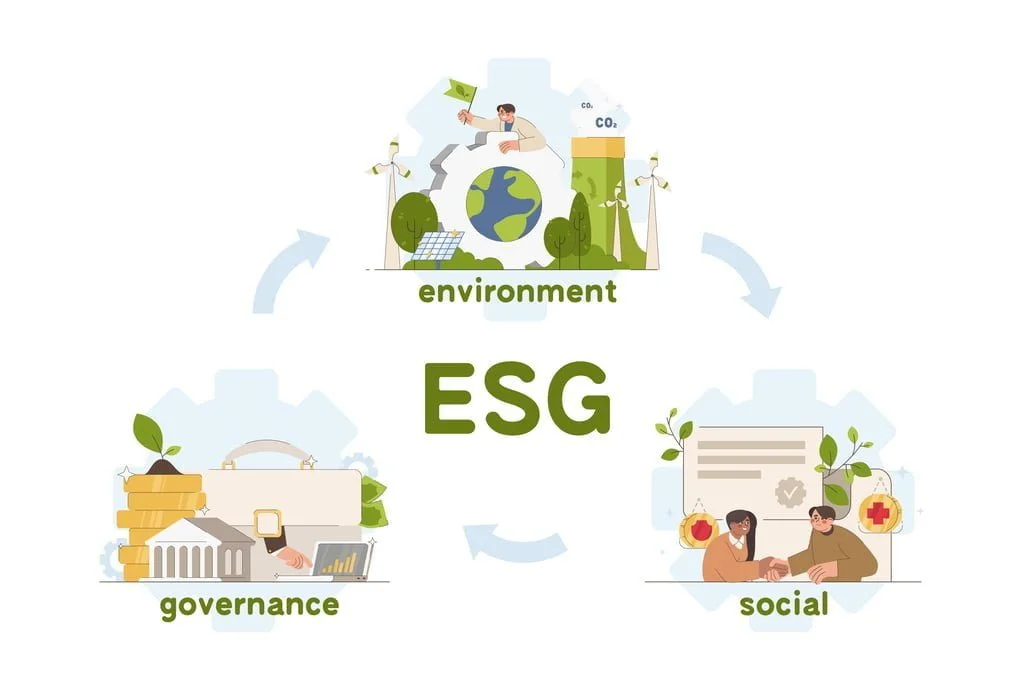
Image by redgreystock on Freepik
In simple terms, ESG refers to a set of criteria used by stakeholders, particularly investors, to assess the impact of Environmental, Social, and Governance factors on a company, alongside its financial performance.
While there are no global standards for ESG metrics, guidelines exist from organizations such as the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), and United Nations Global Compact (UNGC). Some ESG metrics are outlined as follows.

The environmental aspect of ESG emphasizes the importance of sustainable energy practices for companies worldwide.
Real-World Applications of Sustainable Energy Solutions
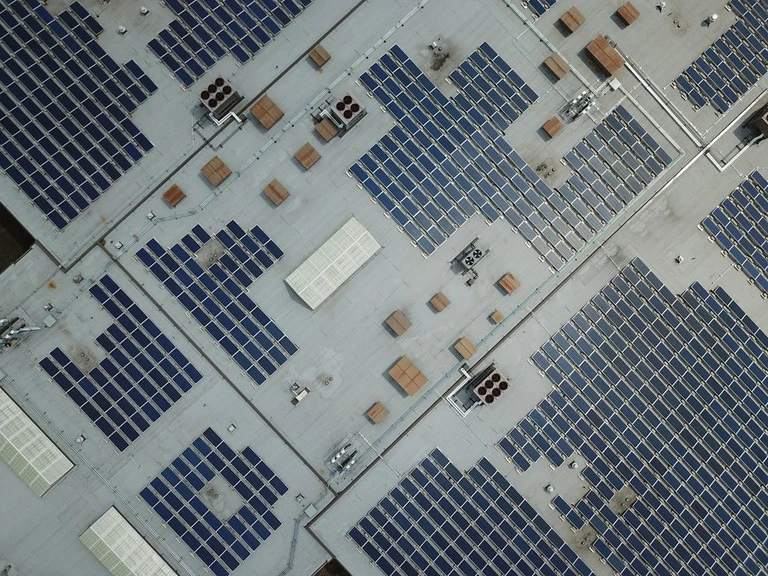
Gigaphoton Inc., a Japanese light sources manufacturer for semiconductor lithography machines, installed 1,100 photovoltaic solar panels on the head office’s roof in February 2023. It is set first to generate power this month (May 2023).
The installed solar panels are forecasted to generate about 460MWh, or 4% of the company’s power consumption annually. The company plans to achieve a 30% use ratio of renewable energy in 2030, which aligns with its commitment to sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint.

Source: Business Wire
Conclusion
Sustainable and renewable energy has become increasingly vital for the global economy and business operations, driven by factors like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria.
By 2030, we anticipate that the use of sustainable and renewable energy will become mainstream, supported by advancements in technology worldwide.



